Diabetes Prevention Day Held in Odesa
Last week, a Diabetes Prevention Day was organized in Odesa for residents, including children, focusing on the prevention and early detection of diabetes.
This initiative was supported by the Department of Health of the Odesa City Council and the Odesa City Health Center.
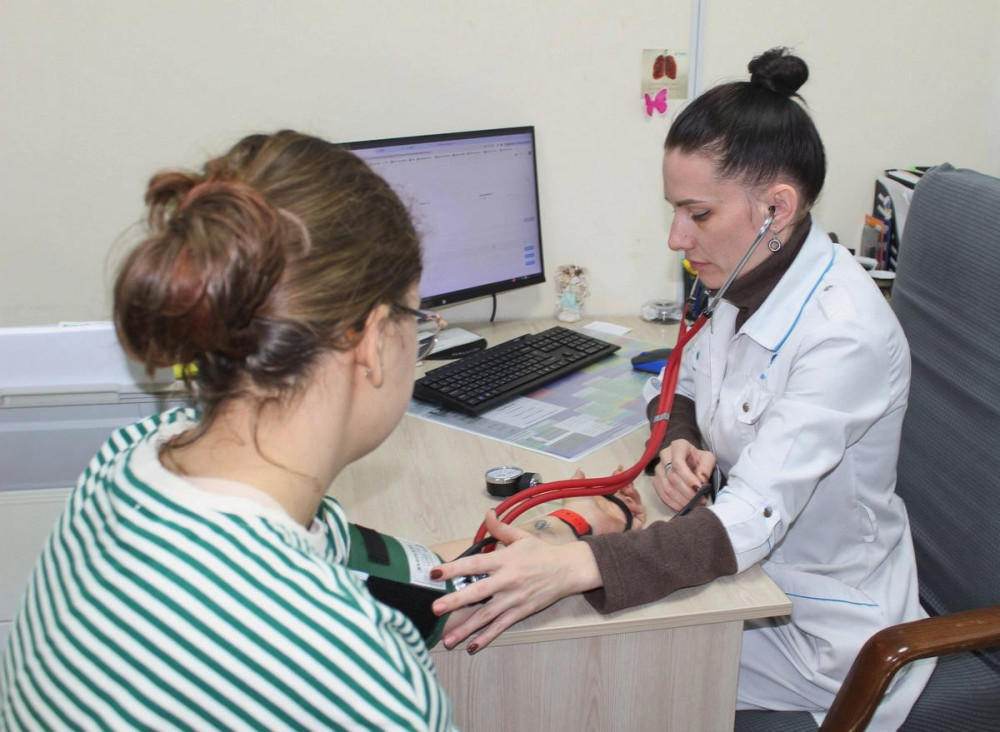
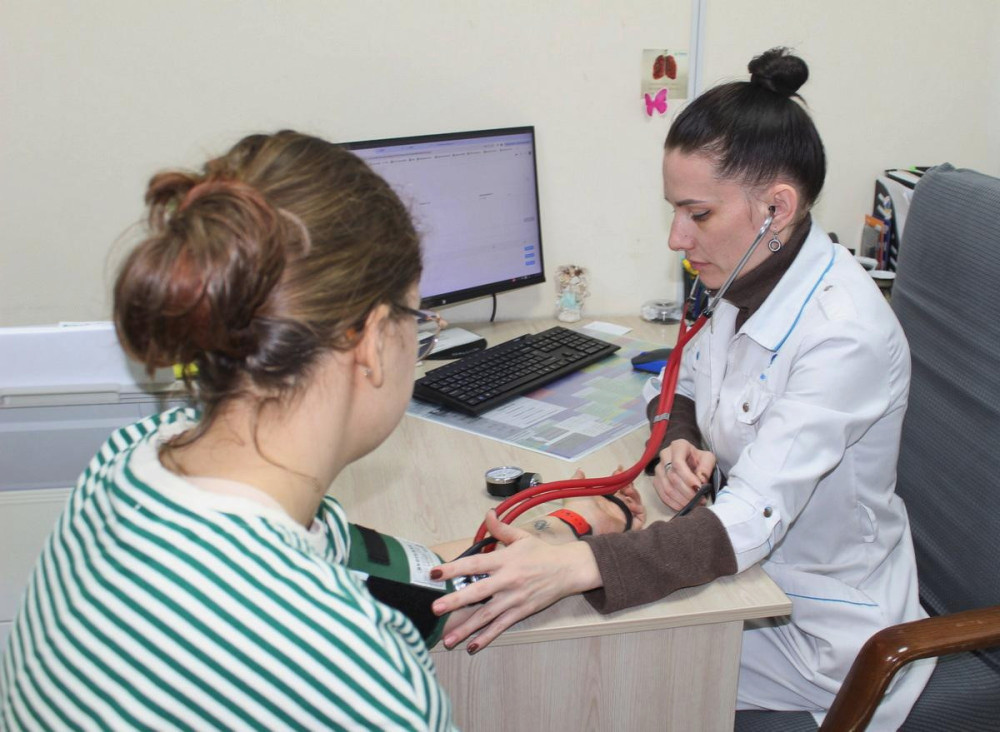
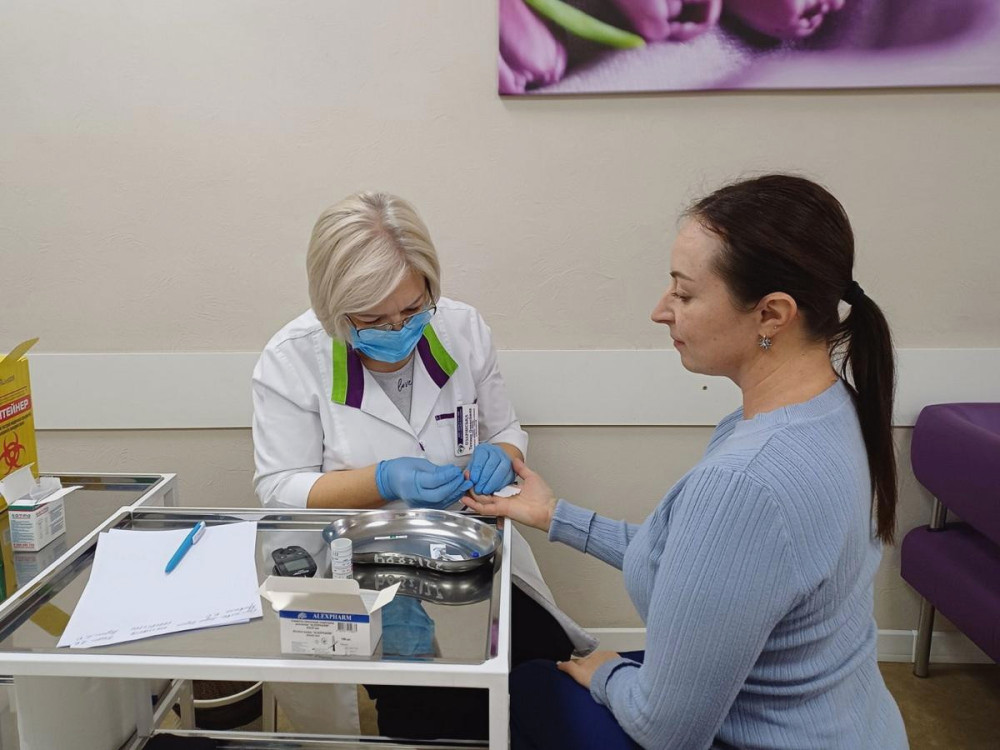
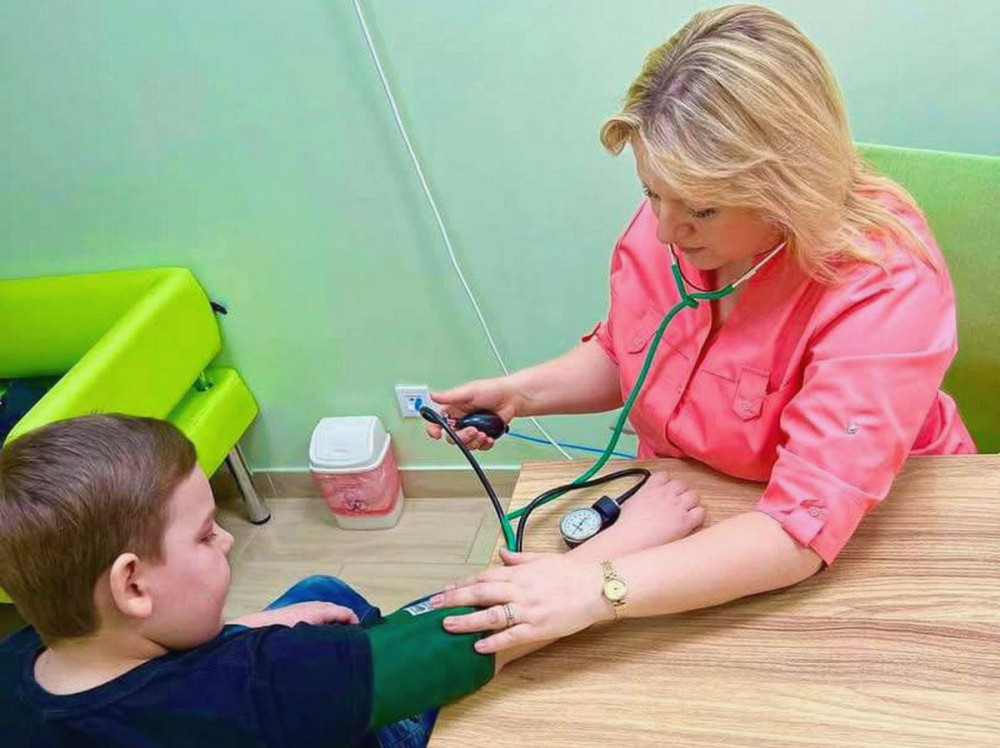
During the event, healthcare professionals measured blood glucose levels, blood pressure, height, weight, and calculated body mass index, providing consultations as needed. Electronic referrals for laboratory tests were also issued.
Additionally, doctors engaged with visitors, educating them about diabetes prevention, risk factors for type II diabetes, and promoting healthy lifestyle habits and nutrition principles.
As a result of the event, 3130 individuals participated in preventive examinations, including 2280 adults and 850 children.
Among the adults, 296 cases of high blood pressure and 161 cases of elevated blood glucose were identified. 467 individuals had a high body mass index, and 227 were referred for further tests.
In children, 10 cases of high blood pressure and 13 cases of elevated glucose levels were detected. 91 children had a BMI above the norm, and 76 were referred for cholesterol testing.
Overall, during the preventive event, doctors conducted 2986 consultations, 706 of which were for children.
***
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, which can lead to severe complications such as heart attacks, strokes, and vision impairment.
Common symptoms of diabetes include thirst, constant hunger, frequent urination, weight fluctuations, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Type I diabetes is insulin-dependent and usually develops quickly in younger individuals, whereas Type II diabetes is linked to insulin resistance and can often develop without symptoms.
Risk factors for Type II diabetes include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, stress, and age-related changes.
Prevention of Type II diabetes:
- Maintain a normal weight — BMI should not exceed 25.
- Be active — engage in at least 30 minutes of physical activity daily.
- Adopt a healthy diet — reduce sugar and saturated fat intake, increase fruits and vegetables.
- Quit smoking.
- Regularly monitor blood sugar levels.